Suitability Modeler widget
The Suitability Modeler widget helps you do the following:
- Find the best location for an activity.
- Predict susceptibility to risk.
- Identify where something is likely to occur.
This widget allows you to combine and weight different layers so you can evaluate multiple factors at once. For example, suitability models help answer questions such as Where are the greatest risks for insect damage? or Where are optimal locations for a commercial development? The answers to these types of questions depend on your input data and the criteria you define from that data.
The Suitability Modeler widget uses fast, web-based weighted raster overlay to generate models from a service. You can start from a blank state of a weighted raster overlay (WRO) service or a preconfigured WRO model. Choose layers, assign weights, and adjust layer classification values to define your analysis. Then, run the modeler, visualize results, and optionally save the result as an item in your organization or portal.
The Suitability Modeler widget, identical to the modeler in ArcGIS GeoPlanner, leverages a special type of image layer known as a weighted overlay service. This type of service is published to ArcGIS Server and added as an item in ArcGIS Online. There are several weighted overlay services provided by Esri and available publicly in ArcGIS Online. These include ecological and physiographic datasets that have global extents. Some of these services are maintained and updated by Esri so your analyses always run using current data. The suitability models created by the Suitability Modeler widget, once exported, are hosted as ArcGIS Online image service layers. These are referred to as weighted overlay model services, or models for short.
Understand weighted overlay
Weighted overlay has three conceptual steps. First, each raster layer is assigned a weight, as a percentage, in the analysis. This allows you to emphasize the relative importance of each layer in the analysis. Second, values within each raster layer are mapped to a common suitability scale. This allows you to compare the different types of information in each raster layer. Third, all raster layers in the analysis are overlaid. Each raster cell’s suitability value is multiplied by its layer weight and totaled with the values of other raster cells it overlays. The result is a suitability value that is used for symbology in the output raster layer.
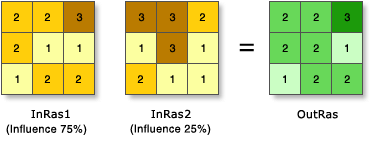 |
In the illustration, the two input rasters have been reclassified to a suitability scale of 1 to 3. Each raster is weighted with a percent influence. The cell values are multiplied by their weight, and the results are added together to create the output raster. For example, in the upper left cell, the values for the two inputs become (2 * 0.75) = 1.5 and (3 * 0.25) = 0.75. The sum of 1.5 and 0.75 is 2.25. The final value is rounded to 2, as the output is an integer raster layer.
Configure the Suitability Modeler widget
-
Add the Suitability Modeler widget to your app.

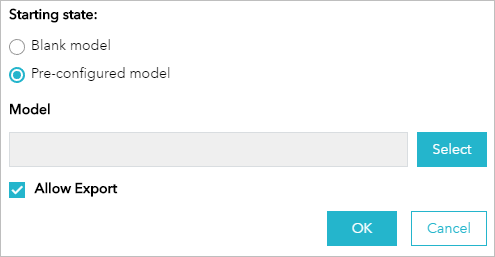
- In the Configuration panel, choose one of the following options for Starting state:
- Blank model—This model allows you to point to a WRO service URL directly. With this approach, users will start from a blank state every time they open the widget. This is a good approach for use cases when the criteria (layer) combinations are also open for experimentation.

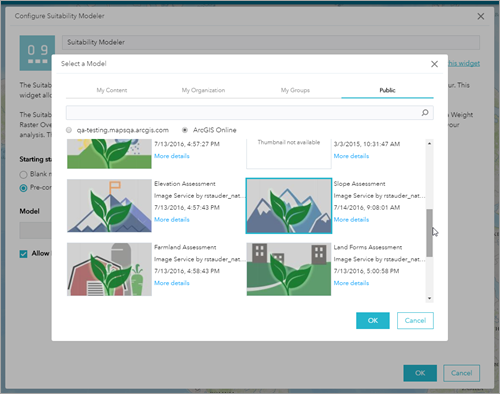
- Pre-configured model—This model allows you to find a WRO model that contains the WRO service on which it is based, the layer combinations, and the weighting. This is a good approach when users are expected to derive new models from an existing model (for example, various stakeholders’ views on risk factors and their respective importance).
- Blank model—This model allows you to point to a WRO service URL directly. With this approach, users will start from a blank state every time they open the widget. This is a good approach for use cases when the criteria (layer) combinations are also open for experimentation.
- For the Allow Export option, decide whether or not users are allowed to export their models after using the widget (storage may consume credits) by checking or unchecking the check box.
- Click OK to confirm the configuration.
Use the Suitability Modeler widget
- Open the Suitability Modeler widget.

- Under the Layers section, check the layers you want to include in your analysis.
You can choose up to 15 layers. Scroll down the list to see all the options.
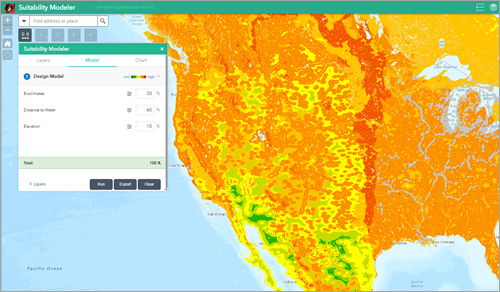
- Click Design Model.
In the Model section, you can assign each layer a relative importance in the analysis by typing a percentage in the percentage (%) text box. The total percentage must equal 100 before you can execute the analysis.
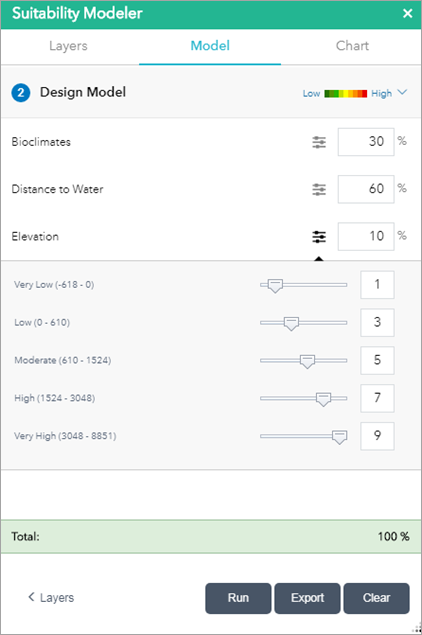
- Optionally, expand each layer and adjust its class weights.
Class weights are how layer values are mapped to a suitability scale. In the example above, the Elevation layer is weighted at 10% and has five classes. Each class is mapped to a suitability value of 1 to 9. The Very Low class (-618 to 0) is mapped to a suitability value of 1. During the analysis, any Elevation value between -618 and 0 is remapped to a value of 1. How you interpret this depends on your criteria. For example, if you are trying to identify areas that can support a flower that grows at higher elevations, a suitability value of 1 indicates that it is unlikely to be found there.
- Click Run.
A rendered WRO model appears on the map.
Once you've run your model, you'll be able to create charting percentages.
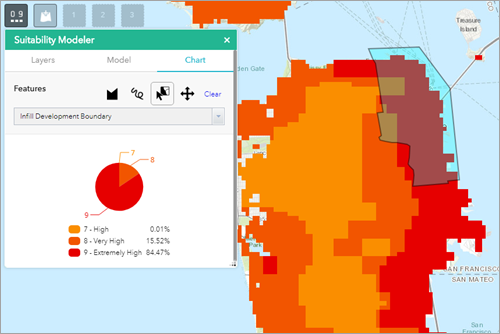
- Select Chart in the Suitability Modeler window.
Choose between the features to create a chart of your model. You can use tools including the following:
- Draw a polygon
- Draw a freehand polygon
- Select from a layer
- Pan
- On the Export dialog box, type a name for your model and click Export.
The Export dialog box closes. The model is processed in ArcGIS Online and is returned as an image layer to the app.
 Note:
Note:The Export option only appears if Allow Export was checked in the configuration.
Weighted overlay models provide a powerful way to visualize and analyze site suitability factors. Based on the shading in your model, you can identify areas of opportunity and risk. The models you create can be further leveraged for real–time feedback in the GeoPlanner dashboard charts. These charts show how your design or other feature layers overlay with assessment layers. This view can help you understand the suitability or risk in your designs and plans.
For more information regarding how to publish your own data for weighted overlay, see the GeoPlanner documentation.